
How To Build Basic Underground Shelter
In preparing for what comes, we give consideration to a great many different potential problems and disasters:
In our personal preparations, we are at the point where we
have and will have food and water, as much First Aid as possible, and our land is
"hopefully" at sufficient elevation to be above any potential flood plain. (4500
feet above sea level) There is no evidence of volcanic activity nearby, but the potential
of earthquake exists, as it does for most of us. Our house is of block, and its ability to
withstand earthquake isn't too good. It could vibrate apart easier than a wood frame
house. So our thoughts turn to shelter, just in case.
We have acquired large, heavy duty tarps, parachute cord and if necessary, we can acquire
20 foot lengths of PVC pipe to make a frame for a dome shelter. However, wind begins to
become an obvious factor in making a decent shelter, and tarps and plastic pipe just
wouldn't work. What to do?
Ideally, one or a few of those Sea Box type shipping containers would be great, but at
US$4,000+ each, that's not within our grasp at this time. Wood frames can withstand a
great amount of wind, but they also have their limits. It came to mind that underground
would be a good place, but not a cave or mine, since the possibility of cave-in is pretty
good.
My grandparents started to build a house in Connecticut back in the late twenties, but as
they progressed, money suddenly dried up and all they had was the basement. They took the
framing for what would have been the first floor, and made it into a roof. My mom grew up
in that "underground" house, and even experienced while there, the worst
hurricane that part of the country ever experienced. While all their neighbors' homes were
literally destroyed by the high winds, my grandparents and family were safe and dry and
warm.
What follows are the plans I have made for a simple box, that can be put, or more likely
built in a hole. Properly covered, it will withstand a great deal of adverse conditions.
Since money is by no means plentiful in our lives, I planned it as simply as possible.
Once decent shelter is achieved, comforts can be added as the materials are acquired. I
say "acquired" because more than half of the supplies we have been able to get
came from means other than purchase. This includes:
So, in the drawing of these plans, I kept in mind that the materials for this box may be acquired piece-meal, and the construction would go accordingly. Here goes.
UNDERGROUND, WATERPROOF? WINDPROOF? EARTHQUAKE RESISTANT? SHELTER
Most of us are physically able to dig a hole by hand with
a shovel, pick and pry bar. The hole has to be about twelve feet wide, by sixteen feet
long. Depth is up to you. The deeper, obviously, the better. Save what dirt that comes out
of the hole, as it can be used to cover your box. Based upon experience, in packed soil,
with six inch rock, a four feet deep hole took me four days of unforgettable hard labor.
Many hands make for light work. GET HELP!!
The simplest waterproofing would be by using landscape plastic. Six mil would be the best.
But if that's not available, the heaviest you can get is better than none. You are going
to wrap the entire box in plastic, then fill in the hole around the box and cover it also.
This is why deeper is better. Before you begin putting your frame together, line the hole
with the plastic. You will be assembling the frame over the plastic, so be careful not to
puncture it.
The box, as shown in Figure 1, is made up of five ribs, and two ends.

The box will be seven feet, ten and one half inches wide,
eight feet tall, and eleven feet, ten and one half inches long. The shaft for the entryway
is two feet wide by four feet long by two feet high.
MATERIALS
Here, in the extreme southeastern corner of Arizona, where
building materials are a little more expensive than the bigger cities, the above materials
priced out at $460.00. This does not include the hardware to fasten this thing together. A
roll of black, 6 mil plastic, 20 feet wide by one hundred feet long is $50.00. If plastic
is not available, no reason why a lot of paint and caulk won't work just as good. Worse
case scenario, and if nothing is available, don't cover it.
As far as fastening this thing together, if I have power available, I plan to use 3"
deck screws to fasten the 2x6's together and 2" deck screws to attach the wafer board
to the frame. If there is no power, then a good old hammer and nails will have to do. 10d
cement coat box nails if possible, for everything. The problem with hammer and nails is
that things tend to vibrate and loosen with such a frame. Have a good heavy brace on the
other side of what you're nailing, like an eight pound sledge hammer.
The horizontal members of the ribs and end pieces should be cut to seven feet, ten and one
half inches long. All vertical members are to be eight feet. This allows for the overlap
of the top panels over the side panels. See Figure 2 below.
Construct the ribs and ends, and using the horizontal rails, fasten the frame together.
Everything must work in two feet increments, so the panels will match the frame. Be as
meticulous as you can in making the frame square. Everything will fit better, if you do.
Remember that your panels are four feet wide, and must butt together in the center of the
rib.
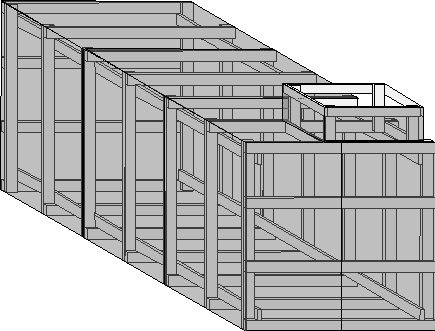
Once the frame is complete, your panels can be fastened to
the frame. Do one end first, then the sides, working from one end to the other.
Before you do the remaining end and the top, cut your floor panels to six feet, ten inches
long, place them inside, and fasten them down. Finish the remaining end.
You can now put the two whole top panels in place, then cut the last panel to fit around
the entryway. The last panel you have will be used to cover the access way chimney. I did
this to help keep debris from falling inside. Make the hatch cover three inches bigger
than the outside of the chimney, and frame it with the last 2x6. It will cover the hatch,
and fastened down with hook and eyes, will provide some security.
I deliberately left out any dimensions for the chimney. Measure and cut to fit.
When you have reached this point, and have a ladder inside for access, finish wrapping the
plastic around everything. Back fill your dirt around the box and cover it about a foot
and a half on top. Pack it down as best you can so it won't blow away.
The inside can be finished with wood frame bunks for sleeping and storage. The exposed
interior studs are easy to work with. Whatever frame work you may add inside, fasten it as
much as possible, to the sides, top and/or bottom. This will serve to reinforce the entire
structure.
Since the entire box is covered in plastic, it won't breath very well. A lot of bodies
generate moisture. With no where to evaporate, this will eventually become a problem in
moister climates. The hatch ventilation may or may not be sufficient.
I have built a few structures similar to this in the past, and as far as strength is
concerned, it is a good plan. If you have questions, feel free to email me at maxine@c2i2.com. Good Luck!
Doug Smith